If you’ve ever wondered what that little chip is on the back of your phone or tablet, wonder no more! It’s called a “chip on glass” and it’s there to provide protection for the camera.
Chip-on-glass technology
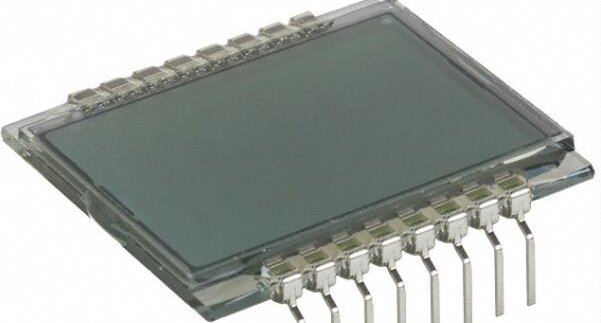
Chip-on-glass (COG) is a type of display technology used in flat panel displays. COG involves mounting a thin film transistor array on a glass substrate. This type of display is typically used in small, portable devices such as mobile phones and digital cameras. COG displays have a number of advantages over other types of displays, including low power consumption, high brightness, and wide viewing angles.
How chip-on-glass technology works
Chip-on-Glass (COG) is a type of LCD technology that uses thin-film transistors (TFTs) on a glass substrate to control the image displayed on the screen. COG panels are typically used in small, handheld devices such as cell phones and digital cameras because they are very compact and lightweight.
COG panels are made up of several layers of materials. The bottom layer is a piece of clear glass, which serves as the substrate. A thin-film transistor (TFT) array is then deposited on the glass. This array consists of an active matrix of TFTs, which are used to control the pixels on the screen. A layer of transparent electrode material is then placed over the TFT array, and a layer of liquid crystal material is placed over the electrode layer. Finally, another piece of glass is placed over the liquid crystal layer to serve as a protective cover plate.
When an electric field is applied across the liquid crystal layer, it twists the crystals and allows light to pass through. The amount of twist can be controlled by varying the voltage applied to the electrodes, which in turn allows for precise control over the pixels on the screen.
The benefits of chip-on-glass technology
Chip-on-glass (COG) is a type of packaging technology used for semiconductor devices. In this process, the chips are mounted directly onto the glass substrates. This has a number of advantages over other types of packaging, including:
- Reduced package size
- Improved heat dissipation
- Reduced costs
COG is often used for small, low-power devices such as memories, microcontrollers, and optical sensors.
The disadvantages of chip-on-glass technology
Although chip-on-glass technology offers a number of advantages, it also has some disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is that the process used to attach the chips to the glass is not very reliable. This can lead to chips falling off of the glass, which can be quite dangerous.
Another disadvantage of chip-on-glass technology is that it is not very eco-friendly. The process of making the chips and attaching them to the glass creates a lot of waste and uses a lot of energy.
Finally, chip-on-glass technology is quite expensive. The chips are made from expensive materials and the process of attaching them to the glass is complicated and time-consuming.
The future of chip-on-glass technology
Chip-on-glass (COG) technology is a fabrication process that involves bonding a silicon chip directly to a piece of glass. This process offers a number of advantages over traditional methods of fabricating integrated circuits, including improved durability, better heat dissipation, and reduced manufacturing costs.
COG technology is already being used in a variety of applications, including cell phones, LCD displays, and other electronic devices. In the future, it is expected to play an even bigger role in the development of flexible electronic devices and “smart” glass products.
How to choose the right chip-on-glass technology
When choosing a chip-on-glass (COG) technology, the key parameters that must be considered are TFT backplane, optical and electrical performance, costs, manufacturing process complexity and reliability. There are many different types of COG technologies available on the market, and the best one for your application will depend on your specific needs.
TFT backplane: The TFT backplane is the critical foundation of any COG display. It determines the overall performance of the display, including optical and electrical properties. The most important factor in choosing a TFT backplane is the pixel architecture — this will determine the number of pixels that can be accommodated on the glass substrate, as well as the maximum resolution and image quality that can be achieved.
Optical and electrical performance: Optical performance includes factors such as contrast ratio, brightness, viewing angles and color gamut. Electrical performance includes things like response time, power consumption and signal integrity. These properties are all determined by the materials used in the TFT backplane and how they are configured.
Costs: The cost of a COG display will vary depending on the size, resolution and materials used. Larger displays or those with higher resolutions will typically be more expensive. The use of more expensive materials will also drive up costs.
Manufacturing process complexity: The manufacturing process for COG displays is relatively complex due to the need to pattern thin films onto a glass substrate. This process can be challenging to master and may require specialized equipment. As a result, it is important to consider whether your chosen supplier has experience manufacturing COG displays.
Reliability: The reliability of a COG display is dependent on both its material quality and manufacturing process quality. Poorly made displays may have issues with defects such as microcracks, delamination or poor solder joints. Make sure to choose a supplier with a proven track record of delivering high-quality products.
The top chip-on-glass manufacturers
The top chip-on-glass manufacturers are leaders in providing high-quality solutions for a variety of industries. Their products are used in everything from medical devices to automotive applications.
The following companies are the top chip-on-glass manufacturers in the world:
3M
Corning
Dow Corning
Franklin Industries
Heraeus Electronic Materials
Hutchinson Technology
Indium Corporation
Jabil
Plexus Corporation
Schott AG
FAQs about chip-on-glass technology
What is chip-on-glass?
Chip-on-glass (COG) is a packaging technology used to create miniature integrated circuits (ICs) by mounting semiconductor chips directly onto the surface of a glass substrate. This technology is often used for small, portable electronic devices such as cell phones and digital cameras.
How does chip-on-glass work?
A chip-on-glass IC is made by bonding a semiconductor chip directly to the surface of a glass substrate. Conductive metal lines are then used to connect the bond pads on the chip to external circuitry. This process can be done using either solder or an adhesive material.
What are the benefits of chip-on-glass technology?
The main benefit of COG packaging is that it allows for very thin, lightweight electronic devices. In addition, COG ICs are less likely to be damaged by shock and vibration than those using other packaging technologies.
What are the disadvantages of chip-on-glass technology?
The main disadvantage of COG packaging is that it can be more expensive than other methods, such as leaded plastic packages or multi-chip modules. In addition, COG ICs are more difficult to repair and replace than those using other packaging technologies.